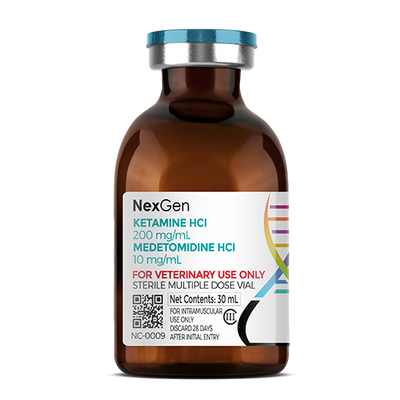
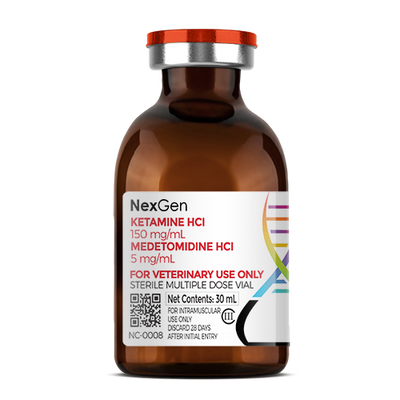
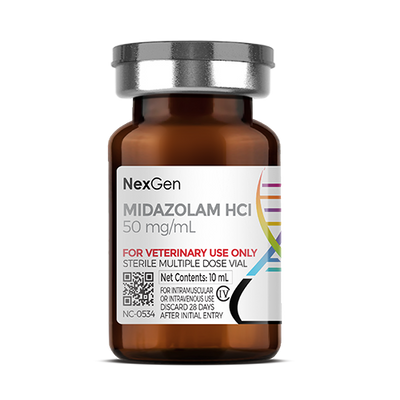
MKBM™ (Medetomidine HCl 20 mg/mL + Ketamine HCl 100 mg/mL + Butorphanol Tartrate 30 mg/mL + Midazolam HCl 20 mg/mL), Injectable Solution, 10mL
Login for pricing
- Brand
- NexGen
- SKU:
- NC-0110
- Product Type:
- Injectable
- Administration:
- Intramuscular
- Size:
- 10ml
- Controlled Substance:
- Schedule CIII
Wildlife practice is a specialized area of veterinary medicine, particularly in the realm of large and exotic hoofstock. Restraining individual animals of these species nearly always requires the use of anesthetic drugs to provide safe, effective immobilization before veterinarians and/or wildlife managers engage in any number of invasive or noninvasive procedures.1,2 Thus, anesthesia plays a critical role in wildlife veterinary medicine. Relocation and other management procedures, preventive medicine, imaging and surgery are among the key interventions typically carried out on wildlife species.
While the study of chemical immobilization has been traced to the South American tribes who used curare-coated arrows to immobilize food animals, the modern chemical immobilization techniques in place today were pioneered beginning in the late 1950s by wildlife managers in South Africa. Many of the species encountered during this period (from the late 1950s through the late 1970s) underscored the vast differences between chemical immobilization requirements across large exotic species.
In the early days of modern chemical immobilization, there was a great deal of trial-and-error as veterinarians and wildlife managers sought the optimal drug combinations to effectively anesthetize wildlife species. Some drugs worked well on certain species, but not on other closely-related species. Other drugs worked very well, but had unforgiving safety margins which could easily lead to the death of an animal. It quickly became apparent that there was no single drug that was ideal for large wildlife species, or even for individual species, since age size, sex, overall health and environmental factors typically play roles in any immobilization scenario.
In recent years, and especially given concerns in the area of conservation and humane treatment, great care has been taken with chemical immobilization protocols and drug development to keep these within safety margins through the use of novel anesthetics, including combinations of true anesthetics, neuromuscular blockers and tranquilizers.2 Thus, modern chemical immobilization techniques have dramatically reduced the side-effects of drugs and mortalities. Additionally, the use of antagonists to anesthetics is now widely employed, as this avoids the undesirable and potentially harmful effects of drugs and facilitates speedy recovery from chemical immobilization events.1,2
Nominal guidelines for chemical immobilization agents to be used in wildlife species generally include the following:
-
Versatility (able to be used in as wide a range of species as is practical)
-
High potency in small volume
-
Wide safety margin
-
Quick induction
-
Calm induction and recovery
-
Reversible effects
-
Rapid elimination
-
Minimal side effects
-
Minimal handling risk for humans
-
Stability
-
Analgesic properties
The MKBM™ Formulation for Exotic Wildlife Species
MKBM™ is an original formulation by NexGen Pharmaceuticals, containing
-
Medetomidine hcl 20 mg/ml
-
Ketamine hcl 100 mg/ml
-
Butorphanol 30 mg/ml
-
Midazolam 20mg/ml
MKBM™ is indicated for the chemical immobilization of numerous large exotic hoofstock species, and is especially efficacious when anesthetizing bongo, kudu, gazelle, eland, as well as other African hoofstock and certain domestic wildlife species.
Where to buy MKBM™
The MKBM™ is an original formulation available exclusively through NexGen Pharmaceuticals. It is indicated for the chemical immobilization of large exotic hoofstock and other exotic species.
MKBM™ carries numerous potential drug interactions. Please consult your veterinarian prior to beginning any treatment regimen.
FOR RX ONLY: A valid prescription from a licensed veterinarian is required for dispensing this medication.
1Arnemo, Jon & Kreeger, Terry. (2018). Handbook of Wildlife Chemical Immobilization 5th Ed. Sunquest Publishing, 2007, 432 pages.
2Nielsen, L. Chemical Immobilization of Wild and Exotic Animals. (1999) Ames, Iowa, Iowa State University Press.
4Bouts T., et. al. Detomidine and Butorphanol for Standing Sedation in a Range Of Zoo-Kept Ungulate Species. J Zoo Wildlife Medicine. 2017 Sep; 48 (3):616-626.