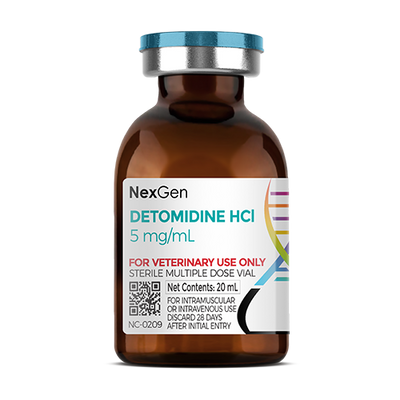
Detomidine HCl 20 mg/mL, Injectable, (10mL)
Login for pricing
- Brand
- Mixlab
- SKU:
- NC-0122
- Product Type:
- Injectable
- Administration:
- Intramuscular / Intravenous
- Size:
- 10ml
Immobilization is necessary in order to safely perform surgical procedures on horses. In most cases, this is achieved through general anesthesia or through a combination of sedation and local anesthesia. Sedatives and anesthetics are powerful drugs which act on various organ systems including the brain, heart, blood vessels and lungs to achieve the desired effects. The interactions of these drugs with organs and systems are complex and sometimes unpredictable. Consequently, treatment with these drugs requires both expertise and an assessment of the clinical status of the horse.
Today, the options for equine sedation allow veterinarians to more safely provide care for horses during standing procedures such as dental exams and joint injections. Some veterinarians prefer to employ heavy sedation rather than a general anesthetic under certain conditions or for certain procedures, such as standing procedures. This is because sedation carries far less risk than general anesthetics.
All sedatives temporarily alter the way the horse’s brain and body works and have a serious impact on the heart and circulatory system.1 As a result, these are all prescription-only medicines.
Anesthetic Drugs for Horses
There are three classes of drugs that are used to sedate horses. These include sedative/tranquilizers, opiates and α-2 (Alpha-2) drugs. Sedative/tranquilizers (such as acepromazine) tend to affect a wide range of body systems. They typically produce mild to moderate sedation on their own, and the effects are variable depending on the horse. This class of drugs also lacks analgesic properties. These drugs can also lead to significant drop in blood pressure, and possess muscle relaxant properties.2
Opiates are generally limited in their efficacy as single drugs, but when combined with other drugs, they can deliver much deeper and smoother sedation than single drugs of most classes. Some of the natural and synthetic opiates have reasonably good analgesic effects, as well as potentiating sedation when combined with other drugs.
Alpha-2 drugs are more widely used in sedating horses as single agents, although they are frequently used in combination with sedative/tranquilizers or opiates. These drugs act by blocking the production of excitatory neurotransmitters—in other words, by “tricking” the body into thinking it’s produced too much adrenaline, leading to a cessation in production of adrenaline.
The Association of Racing Commissioners International Uniform Classification Guidelines for Foreign Substances has designated detomidine a CLASS 3 DRUG.
Where to buy Detomidine HCL
Detomidine is available in the U.S. through several pharmaceutical manufacturers and through veterinary custom compounding companies.
FOR RX ONLY: A valid prescription from a licensed veterinarian is required for dispensing this medication.
1Harris, D. Sedatives and Sedation in Horses. In: pethelpdirect.com, January 8, 2013.
2Taylor, P., et. al. Valuation of sedation for standing clinical procedures in horses using detomidine combined with buprenorphine. Veterinary Anaesthesia and Analgesia, 2014,41,14–24.